Clinical Resources
Ischaemic Chest Pain Pathway SSOU Guideline
Definition
- Chest pain can be caused by a number of different pathologies which may include
- Ischaemic chest pain
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumonia
- Pneumothorax
- Gastritis
- Pericarditis
- Aortic dissection
- Among many others
- Ischaemic chest pain may be stable angina, unstable angina, NSTEMI and STEMI
Admission Criteria
- Pain/ other symptoms resolved
- Risk stratification intermediate or low requiring investigations
- Serious non cardiac cause clinically unlikely
- Stable rhythm
- Stable vital signs
- No acute ischaemic ECG changes
- 1st troponin expected to be in normal range in low risk patients
Exclusion criteria
- Persistent symptoms e.g. pain, dizziness, dyspnoea
- Unstable or abnormal vital signs
- Risk stratification high
- Unstable cardiac rhythm
- Abnormal ECG
- Cardiac enzyme rise
Scoring system
EDACS Emergency Department Assessment of Chest pain score
- Calculate EDACS score via MDCALC
- Chest pain present for >6hrs = single troponin
- EDACS <16 repeat troponin 2hrs
- EDACS >=16 repat troponin 3hrs
Investigations
- FBE
- UEC
- Troponin
- 12 lead ECG
- Consider
- CXR- this may not always be required, consider when patient has last had a CXR and if this is clinically indicated
- D-dimer- if requesting this please refer to “Pulmonary Embolism Pathway”
- Additional
- Requested repeat troponin with appropriate time to be taken
- Repeat 12 lead ECG with second troponin
Suggested medications
Drug
Dose
Frequency
Route
Aspirin
300mg
Once
PO
GTN
300-600mcg
PRN 5min
SL
Paracetamol
1g
PRN 4hrly
PO
Oxycodone IR
5-10mg
PRN 4hrly
PO
Ondansetron
4-8mg
PRN 8hrly
SL/ PO
Metoclopramide
10mg
PRN 8hrly
PO
Specific observations
- Cardiac monitoring
- Report any chest/ arm/ jaw discomfort or shortness of breath to SSOU HMO. Please complete a repeat ECG.
- Repeat ECG to be reviewed by senior SSOU doctor
Consultations
- Consider discussion with cardiology
Discharge criteria
- Resolved pain, no further symptoms
- Unchanged ECG
- No troponin rise
- Follow-up arranged
Admit to hospital if any of the following apply
- Recurrent chest pain or significant symptoms
- ECG changes/ arrythmia
- Troponin rise
Discharge follow-up
- Follow-up testing is not required if patient is <50yo AND has <3 risk factors AND no previous CAD or MI
PULMONARY EMBOLISM
Definition
- A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that develops in a blood vessel elsewhere in the body (often the leg) and travels to an artery in the lung, causing a sudden blockage of blood flow to part of the lungs
- Annual incidence of 0.31 per 1000 in Australia
Admission Criteria
- Stable vital signs
- No O2 requirement
- No increased WOB
- ECG- no signs of right heart strain
- Low or Very Low Risk PESI score
- PERC score >0 (as if 0 will rule out PE)
Exclusion criteria
- PERC 0
- PESI score risk class 3-5
Scoring system
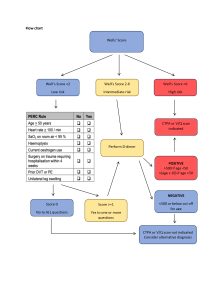
- Calculate Wells score to determine need for d-dimer and CTPA
- If patient low risk calculate PERC score
- If PERC 0 <2% chance of PE indicating no need for further work-up for PE
- If PERC >=1 D-dimer is required
- If patient Intermediate or high risk consider CTPA or VQ scan
- If patient low risk calculate PERC score
- Calculate PESI score to determine mortality risk if patient has PE
- If Very Low Risk or Low Risk PE – can go to SSOU
- If risk class 3-5 requires medical admission
PERC Score
Criteria
Point
Age >= 50 years
1
Heart rate >= 100bpm
1
SaO2 on room air <95%
1
Haemoptysis
1
Current oestrogen use
1
Surgery or trauma requiring hospitalization within 4 weeks
1
Prior DVT or PE
1
Unilateral leg swelling
1
Score
- 0 points or No to all = <2% risk of PE
- >=1 or yes to any= cannot rule out PE
WELLS Score
Criteria
Points
Clinical signs/ symptoms of DVT
3
PE most likely diagnosis
3
Tachycardia (>100bpm)
1.5
Immobilisation/ surgery in previous 4 weeks
1.5
Prior DVT/ PE
1.5
Haemoptysis
1
Active malignancy (treatment within last 6months)
1
Score
- Low risk <2 points- 2-4% probability of PE
- Intermediate risk 2-6 points- 19-20% probability of PE
- High risk >6 points – 50-67% probability of PE
PESI score
Predictors
Points
Demographic Characteristics
Age (yr)
1pt/ yr
Male sex
+10
Comorbid Disease
Cancer
+30
Heart failure
+10
Chronic lung disease
+10
Clinical Findings
Pulse >110/min
+20
SBP <100mmHg
+30
RR >30/min
+20
Temp <36C
+20
Altered Mental status
+60
Arterial O2 sat (PaO2) <90%
+20
Severity index
- The PESI score predicts 30-day all cause mortality
- Very low risk- Risk class 1 (PESI <66) = 0.8%
- Low risk- Risk class 2 (PESI 66-85) = 2.5%
- Risk class 3 (PESI 86-105) = 4.3%
- Risk class 4 (PESI 106-125) = 9.9%
- Risk class 5 (PESI >125) = 27.1%
Flow chart
Investigations
- FBE UEC
- D-dimer if requires as per flowchart
- ECG- looking for signs of right heart strain
- CXR to rule out other causes of chest pain or respiratory symptoms prior to CTPA
- CTPA
- Consider
- pro-thrombotic screen if PE present and unprovoked.
- troponin
Suggested medications
Drug
Dose
Frequency
Route
Paracetamol
1g
PRN 4hrly
PO
Oxycodone IR
5-10mg
PRN 4hrly
PO
Ondansetron
4-8mg
PRN 8hrly
SL/ PO
Metoclopramide
10mg
PRN 8hrly
PO
Apixaban
If CrCl ≥25mL/min
5mg
BD
PO
If CrCl <25mL/min or
Any 2 of the following weight <60kg, age >80yo, Cr >133micromol/L
2.5mg
BD
PO
Therapeutic Enoxaparin
If CrCl ≥ 30mL/min
1mg/kg
12hrly
SC
If CrCl <30mL/min
1mg/kg
24hrly
SC
Specific observations
- Cardiac monitoring
- Report any chest pain or worsening shortness of breath to SSOU HMO.
- If chest pain present please complete ECG and
Consultations
- Discussion with haematology if PE present, patient <45yo and unprovoked PE or if pregnant
- Obstetrics if patient pregnant
Discharge criteria
- If PE present
- Low and Very Low risk PESI score
- Discharge after 4-6hours observation in ED/ SSOU total
- Ensure first dose of DOAC given in ED
- Ensure that patient is discharged with therapeutic DOAC script for 3 months
- Education / counselling for ALL patients commences on anticoagulation either via pharmacy or medical staff
- Refer to haematology clinic
- Symptoms resolved/ much improved
- Observations within normal range
- Follow-up organised
Admit to hospital if any of the following apply
- O2 required
- Submassive or massive PE present
- Troponin rise
Discharge follow-up
- GP
- Haematology if PE present and unprovoked
- Chest pain can be caused by a number of different pathologies which may include
